The industrial internet of things (IIoT) has enabled the digital transformation of industrial facilities the world over. But with that power comes great responsibility, and unfortunately even greater risk for cyberattack. Industry has made clear its need for a conformance scheme that will assure and demonstrate the security of IIoT components.
 In September 2022, ISASecure announced its IIoT Component Security Assurance (ICSA) certification, developed by ISA Security Compliance Institute (ISCI) member companies and inspired by recommendations published in the 2021 study: “IIoT Component Certification Based on the 62443 Standard.”
In September 2022, ISASecure announced its IIoT Component Security Assurance (ICSA) certification, developed by ISA Security Compliance Institute (ISCI) member companies and inspired by recommendations published in the 2021 study: “IIoT Component Certification Based on the 62443 Standard.”
The study, published jointly by ISCI and the International Society of Automation (ISA) Global Security Alliance (ISAGCA), addressed the urgent need for industry-vetted IIoT certification programs, with the goal of determining the applicability of the ISA/IEC 62443 series of standards and certifications to IIoT components and systems. The study examined whether existing ISA/IEC 62443 requirements (and the methods for validating those requirements) were sufficient for the IIoT environment. The results of the study confirmed the feasibility of ISA/IEC 62443-4-1 and ISA/IEC 62443-4-2 for the IIoT environment, with manageable program enhancements (watch the webinar).
ICSA Certification Program Readiness
Many organizations support ISCI, including asset owners from the oil and gas industry and other tier one suppliers across many different industry sectors.
There are nine ISO/IEC 17065/17025 accredited ISASecure certification bodies, offering worldwide ISASecure certification services, as shown in table below.
|
Certification Body |
Geographic Coverage |
Accreditation Status |
|
CSSC |
Japan |
Accredited |
|
Exida |
USA/Global |
Accredited |
|
TUV Rheinland |
Germany/Global |
Accredited |
|
FM Approvals |
USA/Global |
Accredited |
|
TUV SUD |
Singapore/Global |
Accredited |
|
BYHON |
Italy/Global |
Accredited |
|
Bureau Veritas |
Taiwan/Global |
Accredited |
|
TrustCB |
Netherlands/Global |
In progress |
|
Ikerlan |
Spain/Global |
In progress |
ISASecure has agreements in place with seven ISO/IEC 17011 accreditation bodies worldwide, streamlining the accreditation process for new ISASecure certification bodies. They are listed below:
- ANSI/ANAB-North America, Global
- DAkkS, Germany
- Japan Accreditation Council, Japan
- RvA Dutch Accreditation Council, Netherlands
- Singapore Accreditation Council, Singapore
- Taiwan Accreditation Foundation
- A2LA, USA/Global
ICSA Certification Program Description and Scope
There are two types of products that can be certified under ICSA: an IIoT device (i.e., a measurable/influential interface to physical processes and an interface to untrusted networks such as the Internet), and an IIoT gateway (i.e., an intermediary that connects devices on control networks with untrusted networks). Often, IIoT products are both devices and gateways, and therefore an ICSA certification would need to satisfy requirements for both types.
As discovered in the study, the existing ISA/IEC 62443-4-1 and ISA/IEC 62443-4-2 certifications cover about 90% of the desired criteria for IIoT certification. The final 10% of the criteria needed for the ICSA certification includes the following:
- A slight restructuring of capability security levels by creating two certification security level tiers instead of four, as seen in the table below.
- Adding new certification requirements, including:
- 23 new functional requirements, including seven on compartmentalization. Others include supplier root trust in hardware, remote updates and upgrades, and protection from untrusted management traffic.
- New lifecycle requirements, including secure design practices supporting devices failing securely, advanced notification of withdrawal from security update processes, and the Security Maintenance Audit (SMA) as described in more detail below.
- Removing some existing certification requirements in ISA/IEC 62443-4-2, including:
- CR 1.7 RE(1), or the requirement of password generation and lifetime restrictions for human users, due to periodic password changes no longer being considered a best practice;
- CR 2.1 RE(3), or the requirement of supervisor override, due to it not being useful for limited device functionality (which introduces risk);
- CR 2.1 RE(4), or the requirement of dual approval, due to its lack of use in many cases; and
- CR 3.9 RE(1), or the requirement of audit records on write-once media, due to records typically being sent to other systems.
- For existing requirements being used for the ICSA certification, refining the evaluation methods specifically for the IIoT environment.
- For example, a 4-2 requirement states that if you are subject to a denial of service (DoS) attack, you cannot lose the operation of essential functions in your product.
- Here, in an ICSA certification context, the certifier should verify that if there is a DoS attack that takes out the interface to the untrusted network, that essential functions of that component are still operational (i.e., the same requirement, but specific to an IIoT use case).
- CR 1.7 RE(1), or the requirement of password generation and lifetime restrictions for human users, due to periodic password changes no longer being considered a best practice;
Transforming ISA/IEC 62443 Capability Security Levels into ICSA Certification Tiers
As seen in the table below, security levels are determined by the potential attacker and the circumstances of the attack, and security features are allocated to those levels. For example, a Level 1 attack may be a “mistake,” in that it may not be intentional or is otherwise very low risk. On the other hand, a Level 4 attacker may potentially be a nation state that is very highly motivated and skilled to disrupt control systems. 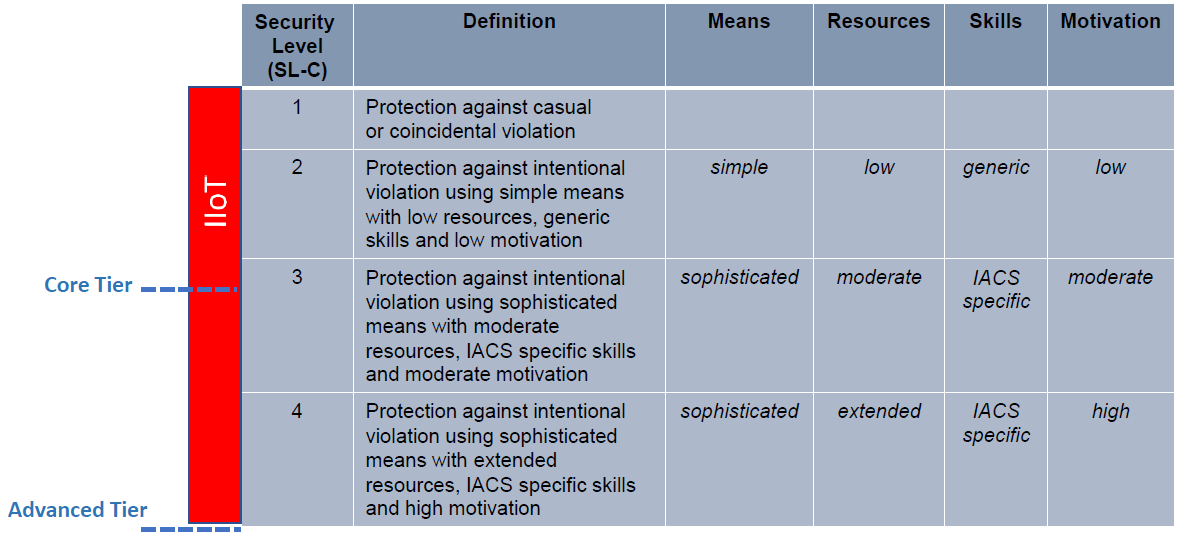 Upon review, it was determined that certifiers are looking more towards intentional, oftentimes sophisticated attacks. For that reason, a “core” tier for basic ICSA certification does not focus on Level 1 and instead begins a little above Level 2 into Level 3 for existing ISA/IEC 62443-4-2 requirements. The “advanced” tier addresses the requirements of 4-2 with the intention to protect against the highest level of adversary, as seen with Level 4.
Upon review, it was determined that certifiers are looking more towards intentional, oftentimes sophisticated attacks. For that reason, a “core” tier for basic ICSA certification does not focus on Level 1 and instead begins a little above Level 2 into Level 3 for existing ISA/IEC 62443-4-2 requirements. The “advanced” tier addresses the requirements of 4-2 with the intention to protect against the highest level of adversary, as seen with Level 4.
Introducing the Security Maintenance Audit (SMA)
The addition of SMA to the ICSA certification addresses the concerns that end-users/asset owners typically have on the “security future” of a product years after certification. (Note that passing SMA is required to maintain an ICSA certification.)
The security maintenance audit (SMA) recommends that the certifier provides ongoing surveillance of the maintenance of product security years into the future, since certain practices in ISA/IEC 62443-4-1 cannot be fully evaluated for the future in the initial ICSA certification, such as defect management (DM) or security update management (SUM). The inclusion of SMA into the ICSA certification provides a time-driven evaluation of specific, key DM/SUM practices for products after the initial ICSA certification, typically one year after, then every three years thereafter. For example, if the supplier had a pattern of not addressing user-reported security issues or fixing known vulnerabilities in a reasonable timeframe, that would be an issue for the SMA.
Further Resources
Additional resources and information about the ISASecure IIoT Component Security Assurance (ICSA) certification are available:




